Our Favorite Directorial Left Turns

On March 18th, Jeff Nichols’ Midnight Special hits theaters. The film, which follows a boy with supernatural abilities getting hunted down by various groups eager to study or exploit him, is a major departure from the rest of Nichols’ filmography. With Shotgun Stories, Take Shelter, and Mud, Nichols showed an interest in small, modest-scaled dramas about internal (Take Shelter) and external (Shotgun Stories) battles in the Southern United States. Now, Nichols has elevated himself to a different, bigger stage: Midnight Special is a full-on, big-budget (compared to his earlier films, that is) sci-fi that has already received comparisons to Steven Spielberg’s work.
Nichols is far from the first director to make a film outside their perceived wheelhouse, and in anticipation of Midnight Special’s release, we decided to come up with our favorite examples of directors who made a successful shift into new, exciting territory. Read our eleven picks below, and let us know if you agree, disagree, or think we’re missing any directors who deserve to be on this list.
Favorite Directorial Left Turns
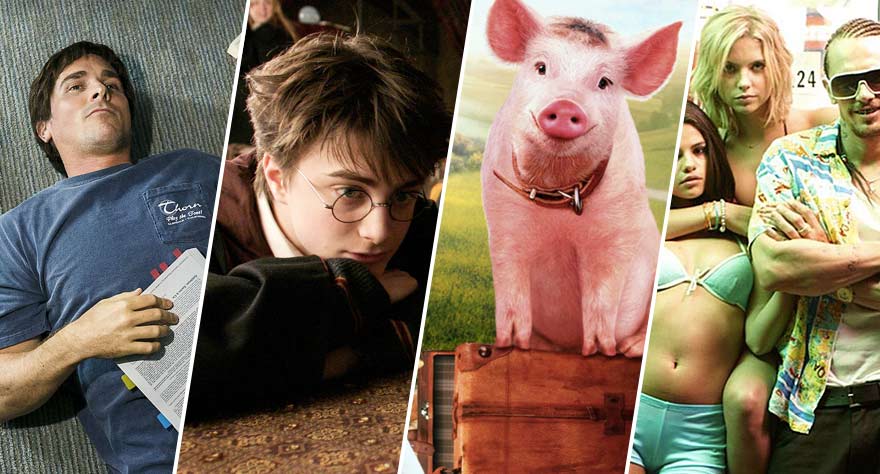
Babe: Pig in the City (George Miller)

Although respectable, George Miller’s post-Mad Max fare—such as The Witches of Eastwick and Lorenzo’s Oil—hardly built on the promise of his influential post-apocalyptic trilogy. In the mid-nineties, Miller’s career took an abrupt change of direction, co-writing and producing the surprise Best Picture nominee Babe (losing out to the far inferior Braveheart). The talking pig was a huge success, and a few years later Miller directed the sequel.
Babe: Pig in the City is far darker in tone than the cozy, bucolic original. Miller pulls out all the stops, creating a trippy atmosphere for his menagerie of chatty creatures, including mice, chimps, pelicans and Mickey Rooney. Ostensibly a family film, it has the bug-eyed intensity of his Nightmare at 20,000 Feet segment in Twilight Zone: The Movie and the baroque imagination of Mad Max: Fury Road. Miller’s lengthy excursion into family film continued with the hit Happy Feet and its sequel, featuring CGI dancing penguins. And just when the scorched landscape of “Mad” Max Rockatansky seemed a distant memory, Miller took another turn onto Fury Road. [Lee]
Bernie (Richard Linklater)
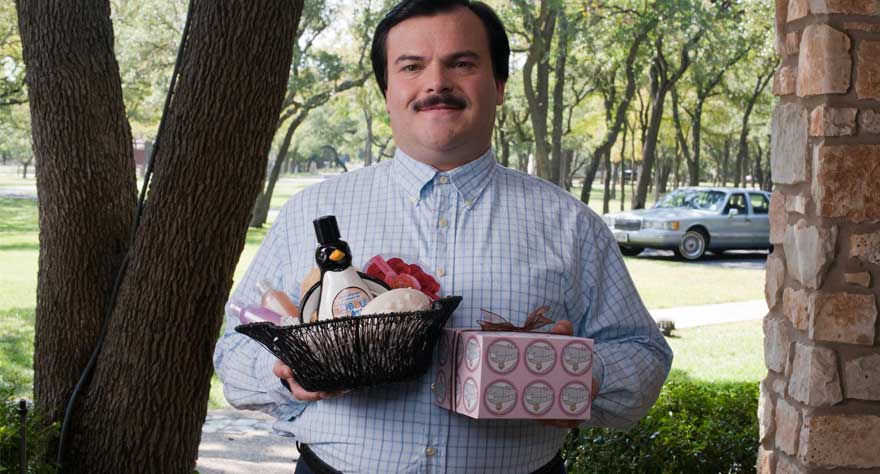

Richard Linklater has always been partial to his home state of Texas, but in his 2011 flick, Bernie, Linklater embraced the east Texas legend of Marjorie “Marge” Nugent’s murder. Linklater’s career is marked with a variety of genres from relatable dramas such as Boyhood and the Before Trilogy to airy comedies like Dazed and Confused, but Bernie served as his only venture into a crime-driven black comedy. Yet, Linklater’s expertise in the understanding of the human condition is manifested in his sympathetic portrayal of Bernie and the often insufferable Marge. Bernie combines many of the elements that make Linklater’s films so beloved, but the presentation is wildly unique. The film combines mockumentary with documentary and comedy with drama in a way that is coherent and captivating. And while Bernie stands out from the rest of Linklater’s work, the quirks present in Bernie are exaggerations of quirks from the rest of Linklater’s filmography, and that is what makes the film such a treat. It’s a departure from the Linklater status quo, but it also represents an artistic evolution and a love letter to rural Texas. [Tanner]
The Big Short (Adam McKay)

The ’60s had the Rat Pack, the ’80s had the Brat Pack, and the ’00s have the Frat Pack, with the likes of Will Ferrell, Vince Vaughn, and Steve Carell in its ranks. One of the key architects of the Frat Pack oeuvre is Adam McKay, writer/director of the Anchorman films, Step Brothers, Talladega Nights: The Ballad of Ricky Bobby, and The Other Guys. You see the pattern. Going off this previous directorial resume, McKay’s doesn’t suggest very much depth. But with his latest effort, The Big Short, he detours from the usual big-laughs-from-little-substance path and takes on material as dense as one can get for a major motion picture: the bursting of the US housing market bubble, and subsequent global economic crisis, that occurred in the mid-2000s. It’s dry, complicated stuff that is plagued by its own jargon-riddled language. McKay (who also co-wrote) presents his smartest humor to date, but also makes the material easy to understand, keeping the film moving at a brisk pace and making brilliant creative decisions—such as fourth wall-breaking and pop-up tutorials conducted by surprise celebrity cameos. The Big Short earned the accolades it received during awards season, and McKay has earned a spot on the list of directors to pay attention to for more than just silly comedies. [Michael]
Harry Potter and the Prisoner of Azkaban (Alfonso Cuarón)
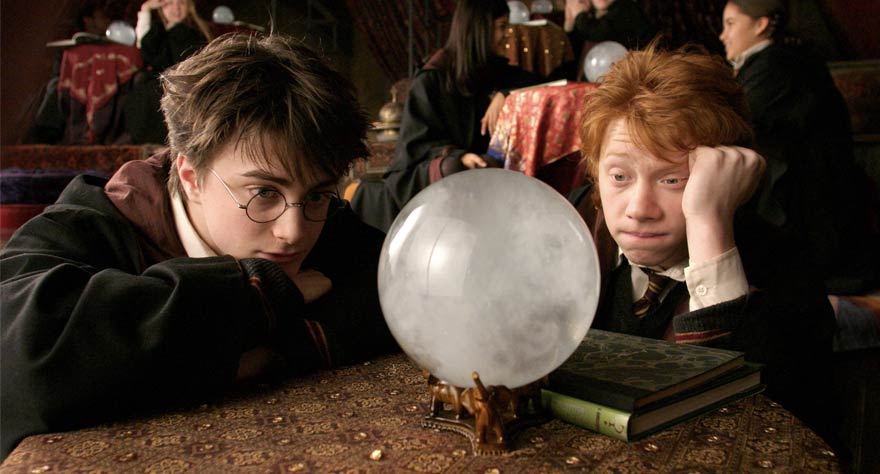

Alfonso Cuarón wasn’t necessarily a stranger to children’s film when he took on the third Harry Potter franchise film, nor to Warner Brothers. He’d directed 1995’s A Little Princess, also a darker toned tale of a child orphan making their way in the world. So while Harry Potter and the Prisoner of Azkaban may not have felt like a left turn for him, for those who think of Y Tu Mamá También when they hear his name, the jump from a horny coming-of-age road trip film to a beloved magical series was jolting. But it isn’t really if one thinks about it. Picking up where Chris Columbus left off in the first two films, Cuarón picked the perfect film of the series to take on. This is where Harry’s journey gets remarkably dark, with his family’s past and secrets he was formerly too young to grasp finally get revealed. He has to choose to face the threats that heretofore came looking for him, AND turn 13. Scary stuff. Cuarón gave the film much needed relevancy, having characters wear modern clothing and letting them interact more with the non-magical world. He gave the Harry Potter series the backbone it lacked and a magic that felt more enticing, simultaneously pleasing book fans and pulling in those who’d previously written the series off as kid stuff. Cuarón knows how to get hearts pumping (Gravity) and feelings flowing (Children of Men), and his approach was a huge success for what is now among the top five film franchises in history. [Ananda]
Hugo (Martin Scorsese)
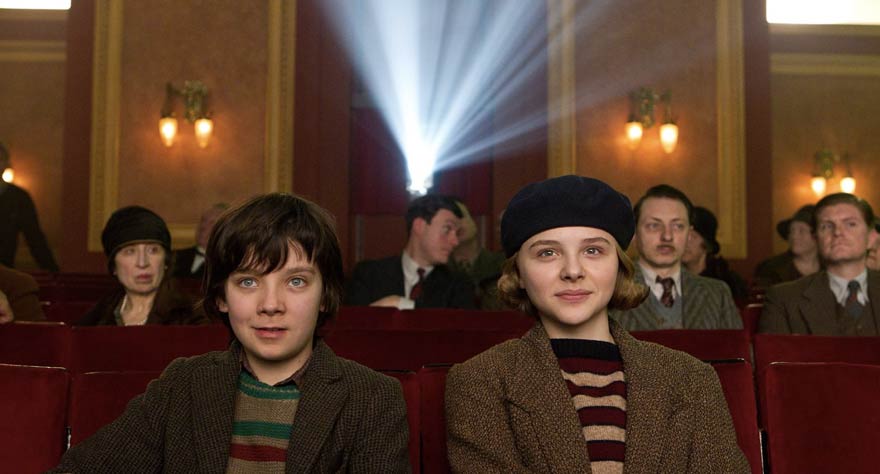

Roger Ebert opened his review of Martin Scorsese’s 2011 film with the line, “Hugo is unlike any other film Martin Scorsese has ever made.” As a director who’s known for his gritty gangster films (Goodfellas, The Departed, Gangs of New York), Scorsese threw a curveball at audiences by making a big-budget family film. In his extensive filmography, the director has only made a handful of PG-rated films, and none (that I can recall) featuring young children as lead characters. But the main reason why Hugo marked such a huge departure for Scorsese was that it was filmed in 3D, a medium often thought to be gimmicky, especially for a filmmaker who is such a strong advocate for preserving traditional film. But it’s easy to see why he made Hugo considering it’s a love letter to cinema, featuring storylines involving early pioneers of film like Georges Melies and the Lumiere brothers. Scorsese shows how those directors experimented with special effects during the early years of film, and it suddenly dawns on you why he decided to make Hugo in 3D. And to top it off, he adds a great message about the importance of preserving film. It’s rare that a filmmaker can make a film like this; one that’s so close to their heart, so much different than their previous work, and yet be easily accessible to every age group. Hugo is that film. [Dustin]
Li’l Quinquin (Bruno Dumont)
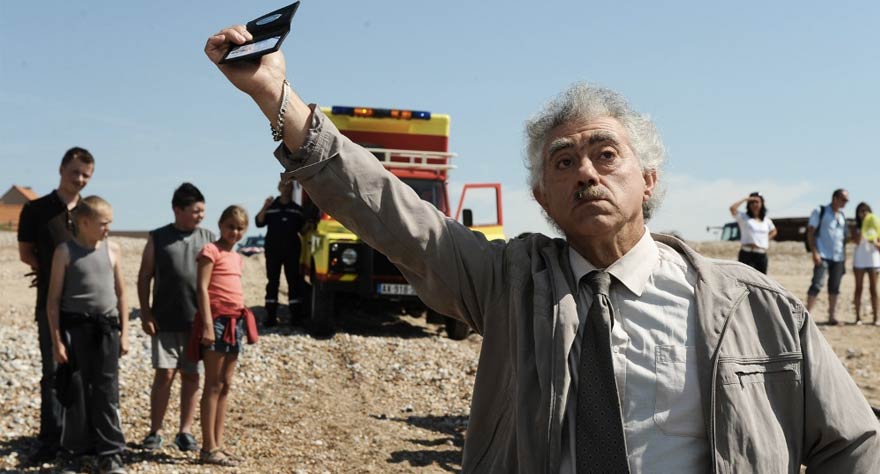

Early on in his career, Bruno Dumont was labelled as an enfant terrible for several reasons: showing unsimulated sex scenes in his films, using sudden, brutal violence, a rigid form that can drive people mad or put them to sleep, and an ability to generate provocative questions about hot button issues like religion and spirituality. Since 2011, after his underrated Hors Satan flopped with critics and audiences, he underwent a bit of a change. His follow-up, Camille Claudel 1915, starred Juliette Binoche, a surprise given his preference to work with unprofessional actors. But it wasn’t until 2014 that Dumont would make his biggest shift yet with Li’l Quinquin, a TV miniseries about detectives trying to find a serial killer in the French countryside. The series marks Dumont’s first attempt at making an outright comedy, and it works like gangbusters (some sequences in here are so unhinged it’s impossible not to choke from laughter). But the biggest surprise of all was that Li’l Quinquin turned out to be Dumont’s biggest success to date, smashing TV rating records in France and getting renewed for a second season. While it’s a definitely left turn for the director, it’s the furthest thing from a compromise, and Quinquin will hopefully mark the beginning of a new, more exciting phase in Dumont’s career. [C.J.]
Spring Breakers (Harmony Korine)
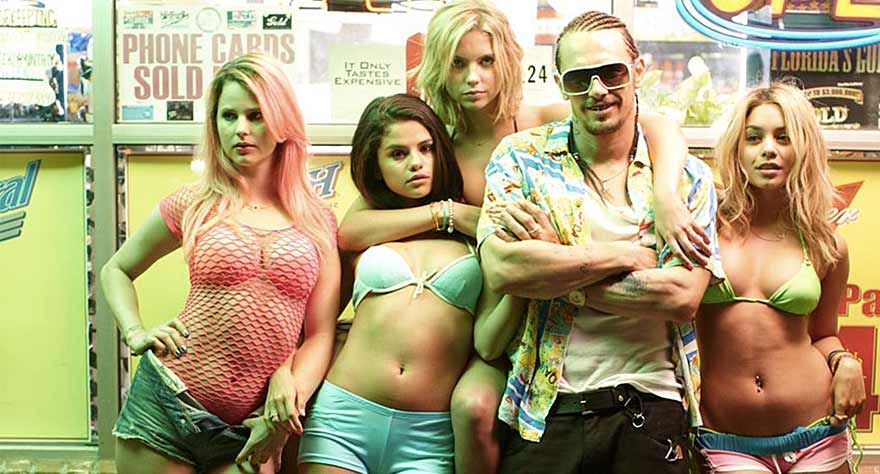
Before the release of the star-studded and fluidly structured Spring Breakers, Harmony Korine wasn’t well-known to general audiences. His filmography had been comprised of works like the deeply strange Gummo, the minimalist but bigger-budgeted Mr. Lonely and the chaotic, dadaist Trash Humpers. Korine wouldn’t go on to direct another film until almost half a decade later, and when he would, he wouldn’t be returning to execute Spring Breakers with the deceptively simple formal qualities of his previous three features. Instead, he hired Benoit Debie (primarily known for his collaborations with Gaspar Noé) as his cinematographer, gathered composer Cliff Martinez and popular dubstep artist Skrillex to work on the score, and cast household celebrities such as James Franco, Selena Gomez, Vanessa Hudgens & Ashley Benson to co-star alongside his wife, Rachel Korine. The end result is a pure sensory overload, constituted by a rich color palette, a free-flowing camera and editing style, and some of the sharpest social commentary to emerge from the American film scene in years, if not decades. [Eli]
The Straight Story (David Lynch)
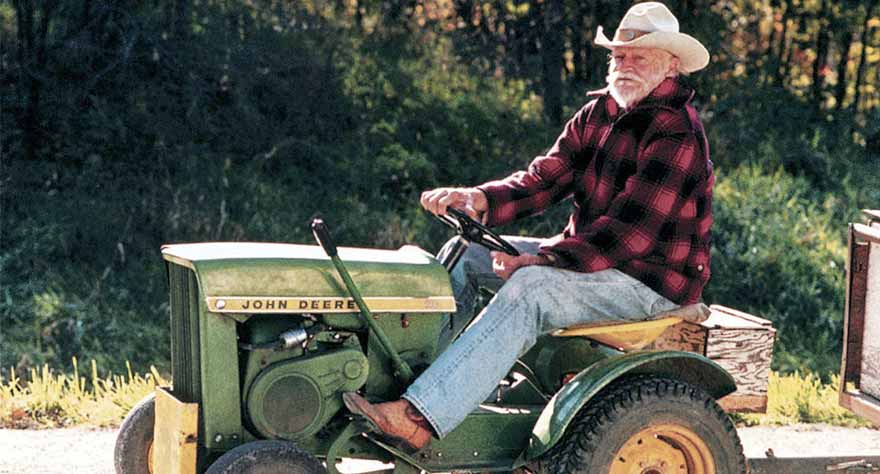

David Lynch has cemented himself as one of the most idiosyncratic filmmakers of our time, tainting our eyeballs with visions of severed ears in the grass, people-sized rabbits doing chores, and Dennis Hopper spitting and spluttering like a loon. Lynch’s films are about as weird as they come, but when asked, the director called his G-rated 1999 heartland drama The Straight Story his “most experimental film.” While it sounds strange at first listen, in the context of the nightmarish sprawl that is his larger oeuvre, the assertation rings loud and true. Nearly every aspect of the film is antithetic to the core concepts of his other works: instead of smashing Americana to pieces, he celebrates it; rather than delivering shocks of violence and sex, the movie is squeaky clean and has no artsy tricks up its sleeve. Richard Farnsworth, in his Oscar-nominated final performance, plays Alvin Straight, an aging man who travels 320 miles from Iowa to Wisconsin on his John Deere (only in Lynchian context is this part bit considered “not weird”) to see his dying brother. Lynch’s broodiness is eschewed here, his visual flair instead working in support of a sweeping road story of love and devotion set along the cornfields and foothills of the good ol’ U.S. of A. Surprisingly, the film has Lynch’s fingerprints all over it despite the conventional tone and narrative. For a one-time affair, the wavy-haired madman plays it straight, and it works astonishingly well. [Bernard]
The Wind Rises (Hayao Miyazaki)
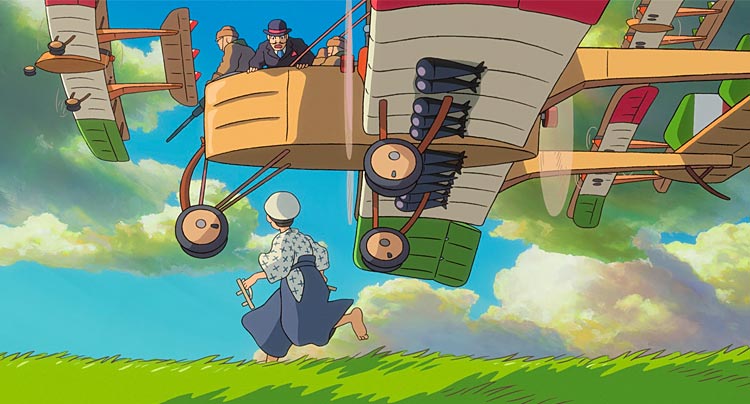
Hayao Miyazaki, the creator of films such as Spirited Away and My Neighbour Totoro, is best known for his beautiful depictions of fantasy and ability to bring imaginary worlds to life on screen. Therefore, The Wind Rises comes as an unusual project from the Japanese animator, acting as a realistic piece of fiction whilst enfolding historical events into its narrative. It’s a fictional biography of Jiro Horikoshi, the designer of the Japanese Zero fighter plane in World War II, and yet it focuses mostly on Jiro’s dreams of flying, rather than the grim realities of his creations. From its terrifying rendering of the Great Kanto earthquake in 1923 to its frequent references to Japan’s involvement in the Second World War, the film is never unaware of its exact place in history. However, The Wind Rises never allows this history to overshadow its message about inventions and possibilities. All the more interesting is the film’s place as Miyazaki’s final feature film, inevitably creating a parallel between himself and the young Jiro, both of whom are artists at their core; men with creative aspirations, but whose works are bound to be consumed in ways they did not intend. Reviews suggest that The Wind Rises is not critical enough of a man who designed machines for war, and yet Miyazaki’s films—often considered children’s tales—have always had a moral message. It seems his final film is a reminder that, once a creation leaves its author’s hands, its fate is as much our responsibility as it is theirs. [Pavi]
The Wrestler (Darren Aronofsky)
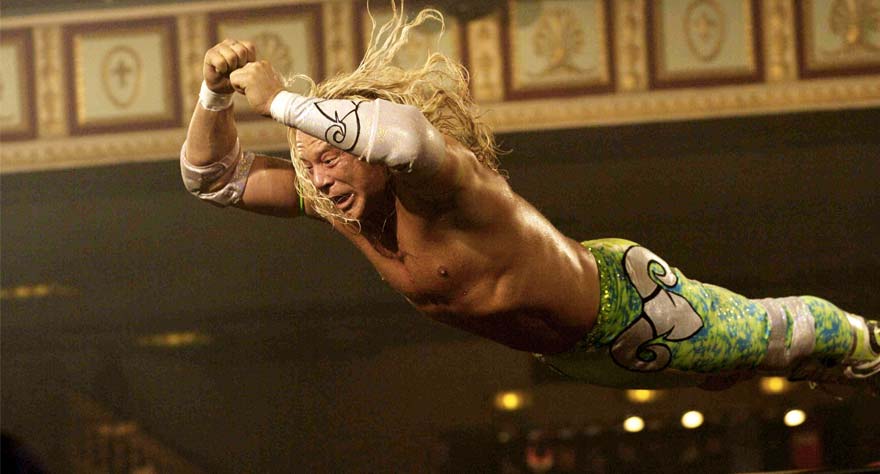

Prior to 2008, Darren Aronofsky had established a consistently heady, kaleidoscopic aesthetic in his work. From the Lynchian surrealism of Pi to the hyperkinetic chaos and visceral impact of Requiem for a Dream to the ambitious, centuries-spanning spiritual epic that was The Fountain, one might’ve thought they had him pegged down as a filmmaker. However, while The Wrestler certainly carries a few subtle hallmarks of Aronofsky’s style and thematic interests, it’s a more stripped-down, genuinely gritty picture than anything the director has attempted before (or since).
A tale of has-beens and former glory is concentrated in the figure of Randy “the Ram” Robinson, a once-famous professional wrestler who has fallen into obscurity. He lives in a trailer, works a menial, unfulfilling job and only finds consolation in his small-time weekend wrestling gigs or in the sympathetic arms of a similarly broken-down stripper. Such a familiar type of story is imbued with refreshing nuance by Mickey Rourke’s unflinching, honest performance and Aronofsky’s neorealist approach. If there was any doubt that the director could make a film expressing unglamorous realities and raw human truths without the stimulation of technical dazzle and flamboyant flourishes, this movie surely puts those concerns to rest. Despite it being a bit of an anomaly in Aronofsky’s career, The Wrestler might just be his greatest work to date. [Byron]
X-Men (Bryan Singer)
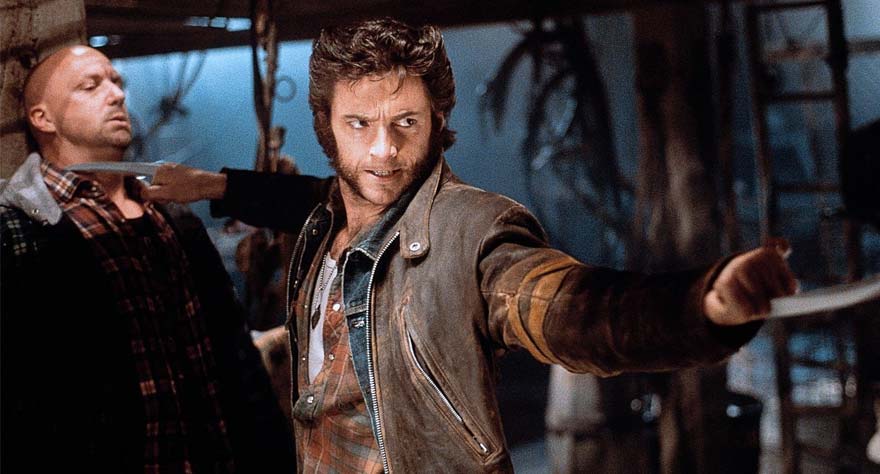

Since Jeff Nichols’ latest studio venture has inspired this feature, I’ve chosen another all-American director, who was also in his mid-30s when he made the quantum leap from small scales and modest budgets by hitting the sci-fi switch. Bryan Singer’s big break came with cult classic crime thriller The Usual Suspects in 1995 where an award-winning screenplay and unforgettable performances bolstered the director’s work enough for 20th Century Fox to have a meeting about it. The character-driven student-teacher Stephen King drama Apt Pupil came next in 1998, but Fox had reportedly already approached Singer for X-Men. He turned it down, made Apt Pupil instead, was courted again—this time by good friend Tom DeSanto—only to finally sign on and set the course for the modern film age of superhero dominance we’re currently (suffering) in.
For the first time in his career, Singer worked with special effects, a budget of $75 million, and in the Sci-Fi sandbox where comic book fandom reigns. And boy did he make it work. It’s near-impossible to measure the magnitude of the aftershock this movie created, after grossing over $200 million at the box-office. Hugh Jackman became a star, studios realized that comic book property was a gold mine they could finally tap into, and Singer made such a triumphantly left turn from chamber dramas to splashy blockbusters, he’s never hard to turn right again. By no means the best superhero film, X-Men is still a perfectly entertaining spectacle that turned its director into one of the best comic book helmers working today. I very much doubt Nichols will make the same impact. [Nik]
