Cary Joji Fukunaga Talks ‘Beasts of No Nation,’ Idris Elba, the Power of Surreality
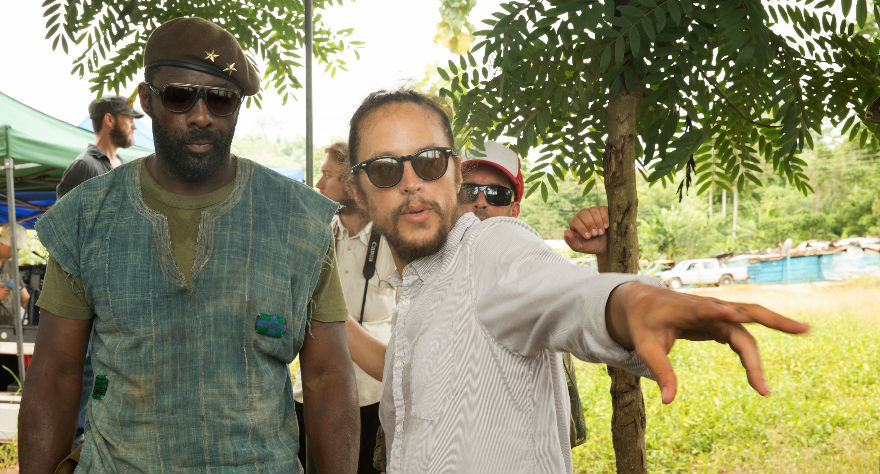

Cary Joji Fukunaga has been steadily building an amazing body of work in his young career. His films Sin Nombre and Jane Eyre earned him the admiration of film critics across the world, and True Detective (a series of which he directed every episode) earned him a rabid fanbase of binge-watchers.
With all eyes now on the Oakland-bred filmmaker, he brings us Beasts of No Nation, a stirring story about a child soldier in West Africa named Agu (Abraham Attah) who’s ushered into manhood by Commandant (Idris Elba), a charismatic rebel leader, after his family is killed in a military raid on his village. The film is stunningly presented with lush jungle imagery and brutally realistic scenes violence that rattle the soul. The observations made on the lives of child soldiers are shocking, but Fukunaga approaches the subject matter with respect and empathy.
I spoke to Fukunaga recently during his visit to San Francisco for the Mill Valley Film Festival. Beasts of No Nation is out in theaters and on Netflix today.
People are very excited about your work and are now following your career very closely. You’ve set the bar pretty high for yourself—your work’s been excellent so far. Is there a lot of pressure now that so many eyes are on you?
Cary: There’s definitely pressure in the sense that expectation is always a pressure. It’d be nice if for every film you made no one knew who you were, took your work at face value and didn’t compare it to Sin Nombre or Jane Eyre. But comparison is also nice in terms of the body of work and seeing how a film fits into it. I’m pretty critical of my own work anyway. No matter what a critic says, I have my own feelings on my work. As much as I want people to like the film, I also know for myself what I’m striving for.
So when people are talking about your movies and shows and you’re all over the Internet all the time, are you so preoccupied with your own critiques of your work that you almost don’t think about external opinion so much?
Cary: No one likes a bad review. Me and all my friends who make movies like to pretend like we don’t read reviews, but we know when people write bad things about our work. It doesn’t matter how many nice things people say about your stuff—as soon as you read something bad, that’s the thing you want to hone in on. You take it personally. It’s also the nature of making something for public consumption. You put yourself out there for critique and evaluation and you have to grow a thick skin, I suppose.
I think you’re improving as a filmmaker with every project. Beasts of No Nation has been gestating for several years now. Was there a point when you almost held off on making the film because you knew working on other things first would benefit the final product?
Cary: Had I made Beasts of No Nation in 2009 or 2010 when I was planning on making it originally, it certainly would have been a different film. There probably would have been aspects of it that would have been better or different depending on my development at the time. Had I made the film ten years from now, it’d probably be different as well. When you make a movie, for better or for worse, that’s what it is. It’s a reflection of your craft, your voice, whatever it is you’re interested in at the time. When you’re writing, you’re so sensitive to your environment. Any little thing can inspire you. Your radar is up and you’re more receptive to things, and that affects what you’re making.
I think Beasts‘ sound design is terrific.
Cary: The sound design was a challenge because we lost our production sound designer about a couple of weeks before we started to mix. We had to start over from square one. Glen [Payne], our sound editor, went to work day and night, trying to put together the sound design. I had a lot of ideas I wanted to try out. For me, sound design is almost if not more important than visuals. It’s part of my fear that when people don’t watch this film at the cinema they won’t experience the film as it was intended to be on an auditory level. If you watch it on your laptop or iPhone, you’re definitely not going to get the sound. The sound was designed to be completely immersive and bring people into that experience of a war itself. To hear those bullets whizzing by, to hear those call-outs, to hear the jungle and the animals—it all gets weaved into it.
I like how surreal the film gets. You seem pretty comfortable going surreal.
Cary: I think True Detective was the first time I ever used slow motion. We did a lot of slow motion, and I was concerned that we were maybe doing too much. There’s objective and inflective camerawork, observational versus when style is implemented for an effect. I’ve always stayed back from doing too much inflective camerawork in my earlier films. Because of the nature of the subject in Beasts, I think you have to be surreal at times, otherwise it’s too brutal. Surreality helps you to not only take in and observe reality, but also not turn off your receptibility to it.
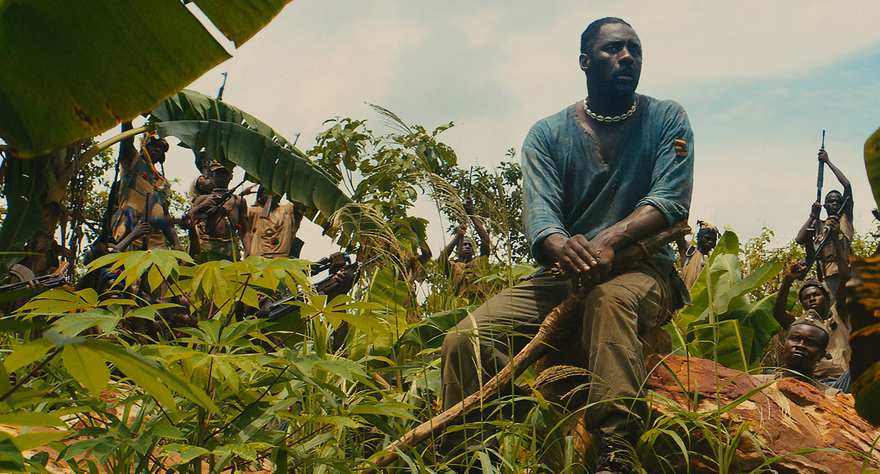
I love the way Idris moves and leans into people and sticks his finger into Agu’s forehead. He’s very imposing.
Cary: A lot of that came from his hairpiece. We tried to figure out a look for him that he’d never done before so that he could really start to disappear into the character. We weren’t going to use prosthetics or anything like that, though Idris even considered something like that. I think the heat of the jungle turned us off from skin prosthetics.
Prosthetics for his face?
Cary: Yeah. We ended up just going with a hairpiece on the back that accentuates the crown of his head. It made him look more like a silverback gorilla. We liked that. The gorilla is a very evolved animal in the jungle. There’s something sympathetic about a gorilla but also something menacing. You want to befriend the gorilla, but there’s not doubt that he’s the king of his domain. I think Idris liked that as well, using a gorilla as a spirit animal.
I like that Commandant and Agu’s internal journeys go in almost opposite directions, with Agu gaining more agency and Commandant losing control.
Cary: That was by design. For me, it was like the death of a father. Agu sees Commandant as he really is. As the influence of drugs and the manipulation of power over Agu becomes less imprisoning, he’s able to find his own voice again. If it helps bring us to his character’s full circle, we need Commandant to fall somehow. Agu needs to see him for who he is. It is a sort of trading of places, isn’t it? But as long as Commandant is out there he has a chance of resurgence.

What was the most challenging day of shooting?
Cary: Every day. [laughs] Every day was so hard. It was a challenge, definitely. It felt like we were compromising ourselves and what we do. It was pretty hard to keep the morale up. For as many unlucky things that happened, there would always be something that’d happen after that that would just bring us right out of the muck. It was very much an up-and-down experience.
You’ve said that you actually enjoy working with children.
Cary: Yeah, I love working with kids. I’ve worked with kids on all my movies, pretty much. There’s something so special about getting a performance out of a kid that’s so unaffected. Abraham in particular is of an age group I’ve only worked with once, in Sin Nombre. It’s a really interesting moment in their time, which is between innocence and awareness. There’s a crossover there where the awareness will continue to grow and the innocence will diminish. If you can catch an actor who has the abilities Abraham has in that moment of time, you get interesting performances.
What’s special about Abraham? What did you see in him?
Cary: It was the observer in him. You could tell that he was a quick learner and that he was always watching. It’s those wheels turning on the inside that you’re looking for. So often you look at somebody and it seems like nothing is going on inside their brain. If you can find an actor with that has that internal life, you can leave that camera on them as long as you want and it’s going to be interesting.
